Welcome back to yet another article titled ‘PEBC evaluating exam sample questions’.
All the best for preparations.
Table of Contents for PEBC evaluating exam sample questions
PEBC evaluating exam sample questions
Question 1: JT is a 35-year-old person who has been experiencing recurrent abdominal pain and discomfort for the past six months. JT reports that the symptoms often improve after defecation but are associated with changes in the frequency and form of the stools. JT alternates between periods of constipation and diarrhea. They have also noticed increased bloating and gas during this period. Their diet and stress levels have remained relatively unchanged. JT is concerned and decides to visit a healthcare provider. Based on the given information, answer the following questions.
Question 1.1: Which of the following is most likely JT’s diagnosis?
A. Crohn's Disease
B. Ulcerative Colitis
C. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
D. Celiac Disease
E. Gastroenteritis
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Question 1.2: Which of the following drugs cannot be used for JT’s constipation?
A. Polycarbophil
B. Prucalopride
C. Linaclotide
D. Pinaverium
E. Eluxadoline
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Drugs used in Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Constipation: Psyllium, polycarbohil, PEG, Lactulose, Linaclotide (if psyllium and polycarbophil fail), Prucalopride, Antispasmodics like Pinaverium, Dicyclomine, or Trimebutine.
Drugs used in Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Diarrhea: Loperamide, Diphenoxylate atropine, Eluxadoline (mu and kappa agonist, and delta antagonist), Cholestyramine, Ondansetron, and Rifaximin.
Question 1.3: Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
A. Gender
B. Age
C. Family History
D. Smoking
E. Psychological Factors
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
Risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome: Gender, age (late adolescence to early adulthood), family history, psychological factors, previous intestinal infections, food intolerances, altered gut microbiota, hormonal changes (especially in women), early life stress, and dietary factors.
Question 2: JT is a 45-year-old man who has been experiencing persistent upper abdominal pain for the past three months. The pain is often worse at night and is sometimes relieved by eating. He also reports occasional nausea and a feeling of bloating. JT has a history of smoking more than two packs of cigarettes daily for the past 20 years. Additionally, JT has epilepsy, for which he takes antiepileptic medication daily. He visited his doctor, who suspects he might have a peptic ulcer. Answer the following questions based on the given information.
Question 2.1: Based on JT’s history, which of the following is the main risk factor for developing a peptic ulcer?
A. High caffeine intake
B. Consumption of fast food
C. Smoking more than two packs of cigarettes daily
D. Use of antiepileptic medication
E. Social alcohol consumption
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Question 2.2: Which of the following is contraindicated for JT’s smoking cessation therapy?
A. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
B. Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT)
C. Interpersonal therapy (IPT)
D. Bupropion
E. Over-the-counter (OTC) herbal supplements
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
Bupropion is contraindicated in seizures and psychosis.
Question 3: ‘JT’s Pharmacy’, a local pharmacy stocking a variety of medications and healthcare products, reported the following financial data over the past year: Beginning inventory value of $150,000, ending inventory value of $200,000, and cost of goods sold (COGS) totaling $600,000. Based on the financial data provided, what is the inventory turnover ratio for City Pharmacy?
A. 2.6
B. 3.4
C. 4.8
D. 5.1
E. 6.0
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B

Image: Explanation of the answer
Question 4: Which of the following is a characteristic symptom of preeclampsia?
A. Hematochezia
B. Hematouria
C. Glucosuria
D. Hyperuricemia
E. Proteinuria
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
A. Hematochezia: Passage of fresh blood through the anus with stools.
B. Hematuria: Presence of red blood cells in urine.
C. Glucosuria: Presence of glucose (sugar) in urine.
D. Hyperuricemia: Elevated uric acid levels in the blood.
E. Proteinuria: Presence of excess protein in the urine.
Question 5: Under which of the following conditions would a pharmacist refer a patient with diaper rash to a doctor?
A. If the rash is mild and appears for the first time
B. If the rash is accompanied by fever or blisters and pus
C. If the rash improves with frequent diaper changes
D. If the rash occurs during hot weather
E. If the rash responds to barrier creams
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Bupropion is contraindicated in seizures and psychosis.
Question 6: JT is a 29-year-old female who comes to the pharmacy with a fungal infection on her feet. The pharmacist wants to check the reference before recommending some over-the-counter products to JT. Which of the following references should the on-duty pharmacist check?
A. CTMA
B. RXTX
C. Cochrane database
D. Health Canada DPD
E. Pubmed
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
CTMA is the reference for self-care and over-the-counter drug recommendations.
Question 7: Which of the following is the correct option to report a drug’s side effects?
A. Canada vigilance program
B. Health Canada
C. NAPRA
D. Marketed products directorate
E. Medeffect website
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
This question can also come as a case.
Question 8: Refugees get their health insurance under which of the following healthcare plans?
A. Interim Health benefits
B. Special Access Program
C. Non Insured Health Benefit Programs
D. Provincial and Territorial Health Care Program
E. Interprovincial Health Coverage
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Interim Health Benefits supports refugees for the first year.
Question 9: Which of the following best describes the roles and responsibilities of CADTH?
A. Conducting clinical trials for new medications
B. Providing evidence-based recommendations on drugs and health technologies
C. Regulating pharmaceutical advertising
D. Licensing healthcare providers
E. Manufacturing pharmaceutical products
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
CADTH is a not-for-profit organization funded by federal, provincial, and territorial governments.
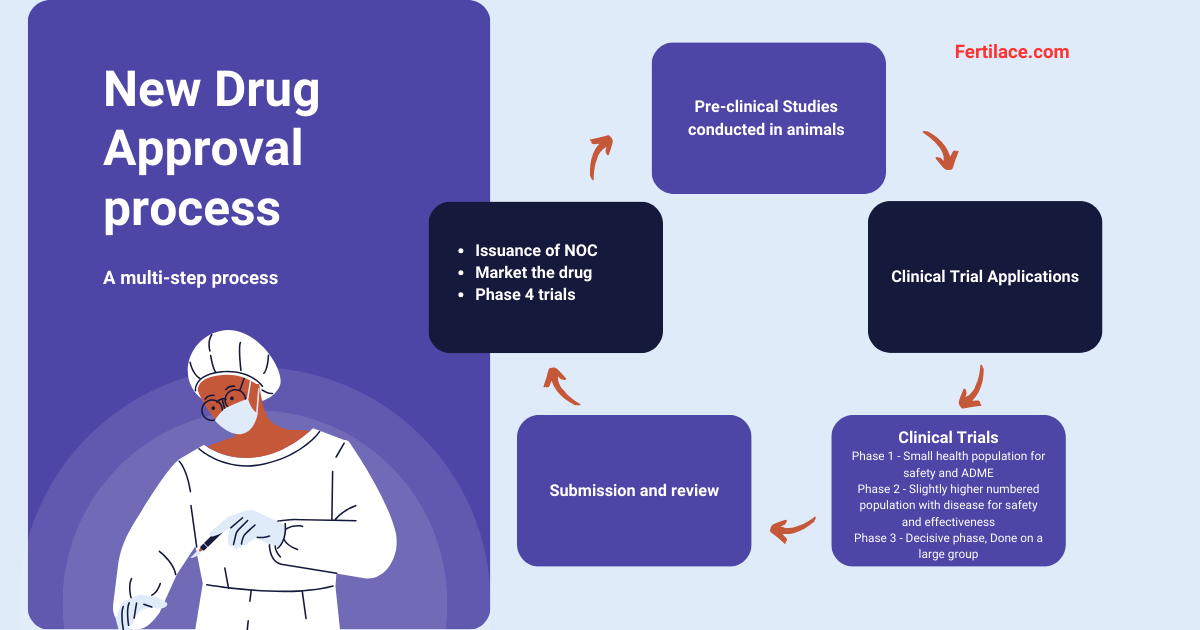
Question 10: Which of the following is the next step after a drug receives Notice of Compliance (NOC) in Canada?
A. Applying for approvals to sell the drug in market
B. Marketing and distributing the drug
C. Applying for patent
D. Conducting Phase 3 clinical trials
E. Apply for Phase 3 clinical trials
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Note for other creators: If you like any images on this blog, feel free to use them. Just give a link to the URL on which you found the image.
Question 11: Which of the following needs to be monitored in a patient who is vomiting constantly?
A. Calcium
B. Potassium
C. Bicarbonate
D. Iron
E. Sodium
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Vomitting – metabolic alkalosis – loss of potassium or hypokalemia
Diarrhea – metabolic acidosis – loss of bicarbonate
Question 12: Tyrosine kinase belongs to which of the following types of enzymes?
A. Ligase
B. Hydrolase
C. Lyase
D. Isomerase
E. Transferase
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Tyrosine kinase is a transferase type enzyme which transfers a phosphate group from ATP to a protein in a cell.
Question 13: Which of the following is a risk factor for stroke in a patient with atrial fibrillation?
A. Age above 65 years
B. History of atrial fibrillation
C. Diet with a low sodium intake
D. BMI of 24
E. DASH diet
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Age, Hypertension, and atrial fibrillation are the major risk factors for stroke. Hypertension is the most important one.
Question 14: If an uneducated person cannot sign a consent form, what is the most appropriate action to take?
A. Skip the consent part and proceed with the procedure
B. Ask a family member to sign on their behalf without explanation
C. Explain the consent form verbally in a way the person can understand and then have them sign
D. Refuse to provide the care or service
E. No need to do anything is consent is implied in this case
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Tip:
The patient cannot read or write, but they can understand. So, the service provider needs to explain the procedure, risks, and benefits. Understand that the person here is uneducated, not incapacitated.
Question 15: A woman with a seizure smokes 2 cigarettes per day. She comes to the pharmacy seeking some help with smoking cessation. What is the pharmacist’s recommendation? – Most Important Question
A. Bupropion
B. Vernacilline
C. Nicotine Replacement Therapy
D. Amitriptyline
E. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Question 16: JT, a pharmacist, is reviewing his recent interactions with patients. He wants to ensure that his actions align with legal and professional responsibilities to avoid liability. Which of the following situations best illustrates JT’s liability as a pharmacist?
A. JT dispenses a medication as prescribed, but the patient has an unexpected allergic reaction.
B. JT accidentally provides incorrect dosage instructions, leading to the patient's overdose.
C. JT gives advice on diet and exercise for general health improvement.
D. JT helps a customer choose an over-the-counter medication for a cold.
E. JT refuses to fill a prescription because he suspects it is fraudulent.
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
The following are 2 different meanings of liability
- Employer’s or employee’s actions leading to harm and negative consequences
- Liability in business terminology is what you owe to other businesses or parties
Question 17: Which of the following is considered the most credible study?
A. Meta analysis
B. Systematic review
C. Randomized Clinical trials
D. Case series
E. Case study
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
| Study Category | Study Type | Mnemonic Phrase |
| Studies of Studies | Meta-analysis | My |
| Systematic reviews | Super | |
| Experimental Studies | Randomized controlled trials | Raccoon |
| Quasi Experimental trials | Quietly | |
| Observational Studies | Cohort studies | Climbs |
| Case control studies | Calmly | |
| Case studies | Confidently |
Question 18: Which of the following is the highest peak in a normal ECG?
A. P wave
B. Q wave
C. QRS wave
D. ST wave
E. T wave
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Question 19: A drug has a volume of distribution (Vd) of 50 liters and a clearance (Cl) of 4 liters per hour. What is the elimination half-life (t½) of the drug?
A. 3 hours
B. 5 hours
C. 8.5 hours
D. 9.5 hours
E. 12 hours
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
Explanation:
The elimination half-life (t½) can be calculated using the formula: t1/2 = 0.693 * (Vd/Cl)
Question 20: A 16-year-old girl comes to the pharmacy and asks for emergency contraceptive pills. For which of the following reasons would the pharmacist refer her to a doctor?
A. Irregular Menses
B. History of emergency contraceptive pill use
C. The girl has headache
D. The girl's age
E. Diarrhea
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 21: A pharmaceutical company is applying for a new botanical product to sell in the market. Which of the following is the correct type of approval for this product?
A. Radiopharmaceuticals
B. Biologics
C. Drug Identification number
D. Vaccine
E. Natural Health Product Number
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Question 22: In a randomized clinical trial comparing two groups investigating surrogate endpoints for diabetes management, which of the following is the most appropriate surrogate endpoint?
A. Blood glucose levels after a meal
B. Death related to cardiovascular events
C. Blood pressure control
D. HbA1c levels
E. Amputation of limbs
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
Question 23: A woman taking levothyroxine became pregnant. Which of the following is the pharmacist’s recommendation for her?
A. Increase the dose of Levothyroxine
B. Discontinue Levothyroxine
C. Decrease the dose of Levothyroxine
D. Switch Levothroxine with Meyhimazole
E. No change is required as Levothyroxine is safe to use in pregnancy
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 24: JT is a 74-year-old male taking Omeprazole with Ibuprofen for his osteoarthritis. Recently, he was diagnosed with anemia. Which of the following statements is true cause for JT’s anemia?
A. Haemorrhage due to prolonged use of NSAIDS
B. Reduced absorption of Vitamin B12
C. Increased RBC lysis
D. High absorption of Cobalamin
E. Deficiency of Iron
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Question 25: Why is Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) added to Diazepam injection?
A. Preservative
B. Universal Buffer
C. Antioxidant
D. Viscosity enhancer
E. Surfactant
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Question 26: A 45-year-old patient has been prescribed itraconazole for the treatment of a fungal infection. During counseling, which of the following instructions should the pharmacist provide regarding the administration of itraconazole?
A. Instruct the patient to take itraconazole with antacids to improve absorption.
B. Advise the patient to take itraconazole on an empty stomach to enhance absorption.
C. Inform the patient that itraconazole can be safely taken with St. John's Wort for enhanced efficacy.
D. Recommend that the patient take itraconazole after meals to reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
E. Assure the patient that itraconazole is not associated with any significant drug interactions.
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Question 27: Which of the following is the most abundant intracellular cation?
A. Sodium
B. Calcium
C. Potassium
D. Magnesium
E. Chloride
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Mnemonic: PISO = Potassium In Sodium Out
Question 28: Which of the following is not used to treat Pseudomonas infection?
A. Ciprofloxacin
B. Amikacin
C. Piperacillin
D. Ceftazidime
E. Vancomycin
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Question 29: Which of the following is a peptide hormone?
A. Cortisol
B. Noradrenaline
C. Thyroxine
D. Aldosterone
E. Glucagon
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Mnemonic for peptide hormones: Important Peptides Affect Thyroid Growth Occasionally Getting Very Good
| Peptide Hormones | Non-Peptide Hormones |
| Insulin | Cortisol |
| Glucagon | Aldosterone |
| Growth hormone (GH) | Testosterone |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) | Estradiol |
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Thyroxine (T4) |
| Parathyroid hormone (PTH) | Triiodothyronine (T3) |
| Oxytocin | Adrenaline (Epinephrine) |
| Vasopressin (ADH) | Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) |
| Luteinizing hormone (LH) | Retinoic acid |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) | Prostaglandins |
Here is a list of all the published articles in this category: Link
PEBC Evaluating exam sample questions pdf link
I will publish more questions like this daily to help you prepare for the PEBC evaluating exam.
If you have any questions, please ask them in the comments section.

Quite impressive and helpful. Keep posting such Q.