Table of Contents for PEBC EE
Questions 1 – 10 to crack the PEBC EE
Question 1: A 55-year-old patient with hypertension is prescribed perindopril as part of their treatment plan. Which of the following is a known side effect of initiating perindopril therapy?
A) Flushing
B) Angioedema
C) Headache
D) Diarrhea
E) All of the above
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Question 2: A retail company has reported its financials for the fiscal year. The total sales amount to $530,000, while the cost of goods sold (COGS) is $350,000. What is the percentage of the gross margin?
A) 10%
B) 20%
C) 25%
D) 30%
E) 34%
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Question 3: A 62-year-old patient undergoing chemotherapy for cancer treatment reports experiencing several side effects, including diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramps. Which of the following symptoms should be of most concern?
A) Blood in stool
B) More than 4 stools daily
C) Nausea lasting more than 4 hours
D) Abdominal cramping for more than 10 days
E) All of the above
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 4: A 45-year-old patient, diagnosed with arthritis, started taking NSAIDs for pain relief and has been experiencing daily heartburn symptoms.
A) Ranitidine
B) Prednisone
C) Cimetidine
D) Antacid
E) Omeprazole
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Question 5: Endocarditis is caused most commonly by which of the following organisms?
A) Gram positive streptococci
B) Gram negative streptococci
C) Gram positive staphylococci
D) Gram positive Enterococci
E) Gram negative Enterococci
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
The Gram-positive bacteria staphylococci 40%, streptococci 20%, and enterococci 10% account for the majority of pathogens causing endocarditis.
Question 6: Which of the following is the correct statement for rheumatoid arthritis?
A) Symmetric joint pain lasting less than 45 minutes and low-grade fever.
B) Occurrence exclusively in weight-bearing joints.
C) Obesity not being a risk factor.
D) Predominantly affecting the elderly population.
E) Involving primarily the large joints such as hips and shoulders.
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Symmetric, for more than 45 minutes in the morning, there is fever, inflammation, and swelling. Happens in both weight-bearing and non-bearing. Obesity is a risk factor.
Question 7: A 60-year-old woman with cancer has been taking hydromorphone for pain management. She is now in the hospital experiencing additional pain and was administered morphine, but she reports no relief. What could be the reason for the lack of response to morphine?
A potentiation
B addiction
C tolerance
D resistance
E toxic effect
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Question 8: An adult female 42 years old has urinary incontinence. She said it has been very bothersome lately and that she could not go out without worrying about if she does not find a toilet. She also added that there is leakage when she coughs or exercises & she has been stressed for the past few days, what kind of urinary incontinence?
A) Stress incontinence
B) Urge incontinence
C) Overflow incontinence
D) Functional incontinence
E) All of the above
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 9: What is it called whereby a pharmacist can ethically refuse to fill a prescription for moral or religious reasons?
a) personal clause
b) notwithstanding clause
c) conscience clause
d) freedom of faith clause
e) mutual respect clause
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Question 10: Ketoacidosis means all of the following except?
a) Hypoglycemia
b) Volume depletion (depleted in Sodium, Potassium, Chloride and water)
c) Acidosis
d) Depressed levels of consciousness
e) Detectable ketones in the urine or blood
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Ketoacidosis is treated by administering insulin and fluids.
PEBC Evaluating Exam Practice Questions 11-20
Question 11: A membrane is placed between two solutions with different concentrations of solute and solvent. What happens?
A) Solute moves from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration
B) Solute moves from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
C) Solvent moves from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration
D) Solvent moves from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
E) No movement occurs
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Question 12: A 65-year-old patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is currently being treated with erythromycin for a bacterial infection. The treating physician is considering adding another antibiotic to the regimen. Which of the following antibiotics can be safely added to his treatment plan?
A) Ciprofloxacin
B) Levofloxacin
C) Clindamycin
D) Amoxicillin
E) Azithromycin
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Question 13: You are a pharmacy manager and have two pharmacists working at the pharmacy, you figured that there is a shortage of Meperidine stock, so you set up a surveillance camera and figure out the one who took this narcotic. what is the appropriate action?
A) Call the pharmacist who was involved in the incidence
B) As a pharmacy manager, use your authority and fire him.
C) Call the regulatory college and report the case
D) Call the Royal Canadian Mounted Police RCMP
E) Report the incidence to the Office of Controlled Substances
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
| Scenario | Action | Follow-up |
| Misconduct by colleague | Report directly to the College of Pharmacy | Not applicable |
| Incompetent pharmacist at another pharmacy | Report to their manager | Maintain contact to learn the outcome |
| Prescription forgery or stolen narcotics | Call the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) immediately | Report to the College of Pharmacy within 10 days |
Question 14: How would you prevent this from happening again?
A) Call the pharmacist who was involved in the incidence
B) Implement employee bag check measures before leaving the pharmacy.
C) Call the regulatory college and report the case
D) Call the Royal Canadian Mounted Police RCMP
E) Report the incidence to the Office of Controlled Substances
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Question 15: Which of the following dosage forms should never be crushed?
a) Sugar coated tablets
b) Chewable tablets
c) Lozenges
d) Osmotic tablets
e) Effervescent tablets
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
Crushing an osmotic tablet will lose its integrity and it can no longer function properly.
Question 16: A patient presents to the emergency department with acute glaucoma symptoms, including severe eye pain, blurred vision, and nausea. What is the drug of choice for emergency treatment of glaucoma?
a) Pilocarpine
b) Acetazolamide
c) Dorzolamide
d) Timolol
e) Latanoprost
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Acetazolamide and methazolamide lower IOP by decreasing the production of
aqueous humor. Their use is normally reserved for emergencies because of significant
side effects.
Question 17: What cause QTc prolongation?
a) Citalopram
b) Amiodarone
c) Nitrofurantoin
d) Amoxycillin
e) Captopril
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 18: JT is a 45-year-old female who was diagnosed with peptic ulcer. Which of the following is a major risk factor for peptic ulcer in JT’s case?
a) Smoking
b) high fat
c) spicy food
d) DASH diet
e) Uncontrolled diabetes
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 19: A 36-year-old male comes to the pharmacy complaining about priapism as it is embarrassing for him. Upon checking his medication records, the pharmacist found that the patient is taking Captopril, Nifedipine XL, and Furosemide for hypertension, Prazosin for nightmares, and Trazodone for sundown syndrome. Which of the following is the most likely cause for this patient’s priapism?
A. Captopril
B. Nifedipine XL
C. Furosemide
D. Prazosin
E. Trazodone
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Question 19: Which of the following drugs cause prerenal failure?
a) Metformin
b) Furosemide
c) Amoxicillin
d) Omeprazole
e) Pravastatin
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Question 20: Which of the following is an example of fast allergic reaction?
a) Contact dermatitis
b) Atopic dermatitis
c) Poison ivy
d) Systemic lupus erythematous
e) Blood group transfusion mismatch
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Questions 21-30 to ace PEBC EE
Question 21: What is the mechanism of action of Digoxin?
a) Increases intracellular Calcium
b) Inhibit beta receptor on heart
c) Xanthine Oxidase inhibitor
d) Norepinephrine reuptake promoter
e) Increases intracellular sodium
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
| Mechanism of Action | Effects |
| Positive Inotropic Effect | Increases myocardial contractility and efficiency by increasing intracellular calcium levels. |
| Inhibits membrane-bound Na+/K+-ATPase, leading to increased intracellular sodium and reduced calcium transport out of cells, facilitating calcium entry via voltage-gated channels. | |
| Negative Chronotropic Effect | Increases vagal tone at the sinoatrial node. |
| Reduces sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system. | |
| Vagomimetic Effect | Induces systemic arteriolar and venous constriction. |
Question 22: Arylpropionic acid-related compounds such as ibuprofen show which of the following?
a) Streoisomerism
b) homologs
c) conformational isomers
d) structural isomers
e) optical isomers
Question 23: Which of the following drugs has more norepinephrine activity than serotonergic activity?
a) Amitriptyline
b) Fluoxetine
c) Nortriptyline
d) Ibuprofen
e) Amoxicillin
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Question 24: The graph mentioned below represents the data of Fluticasone use and the number of physician visits. X-axis indicates number of physician visits in the last 3 months, and
Y axis represents the patient taking fluticasone for asthma. Which of the following statements is true based on the graph given below?

A. The patients who use fluticasone in large concentration visited the doctor less frequently
B. The patients who use fluticasone in low concentration visited the doctor less frequently
C. The patients who use fluticasone in large concentration visited the doctor more frequently
D. No relation can be established between fluticasone use and the number of visits to doctor
E. The data is insufficient forfluticasone use
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 25: What proportions should be used from 2 ointments containing 0.15% and 0.25% dexamethasone, to make 150 mg dexamethasone of 0.2% of dexamethasone?
A. 15 gm of 2.5% and 45 gm of 0.5% dexamethasone
B. 45 gm of 2.5% and 15 gm of 0.5% dexamethasone
C. 25 gm of 2.5% and 35 gm of 0.5% dexamethasone
D. 35 gm of 2.5% and 25 gm of 0.5% dexamethasone
E. 20 gm of 2.5% and 40 gm of 0.5% dexamethasone
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Use allegation method.
Question 26: A patient came with a prescription in his name. However, upon checking, the pharmacist discovered these drugs didn’t belong to this patient. He asked the patient and found that drugs are for his brother who doesn’t have insurance. If you accept this prescription,which of the following principle you violate?
A. Veracity
B. Autonomy
C. Professional competency
D. Incapacity
E. Equality
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Question 27: In comparison between drug A and drug B in the treatment of smoking cessation, drug A reduces the side effects in 44 patients of 500 patients, and drug B reduces the side effects in 56 patients out of 500 patients. What is the odd ratio?
a) 0.7
b) 1.3
c) 2.6
d) 4.5
e) 3.7
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 28: Identify the structure given below from a list of drugs given in the option.
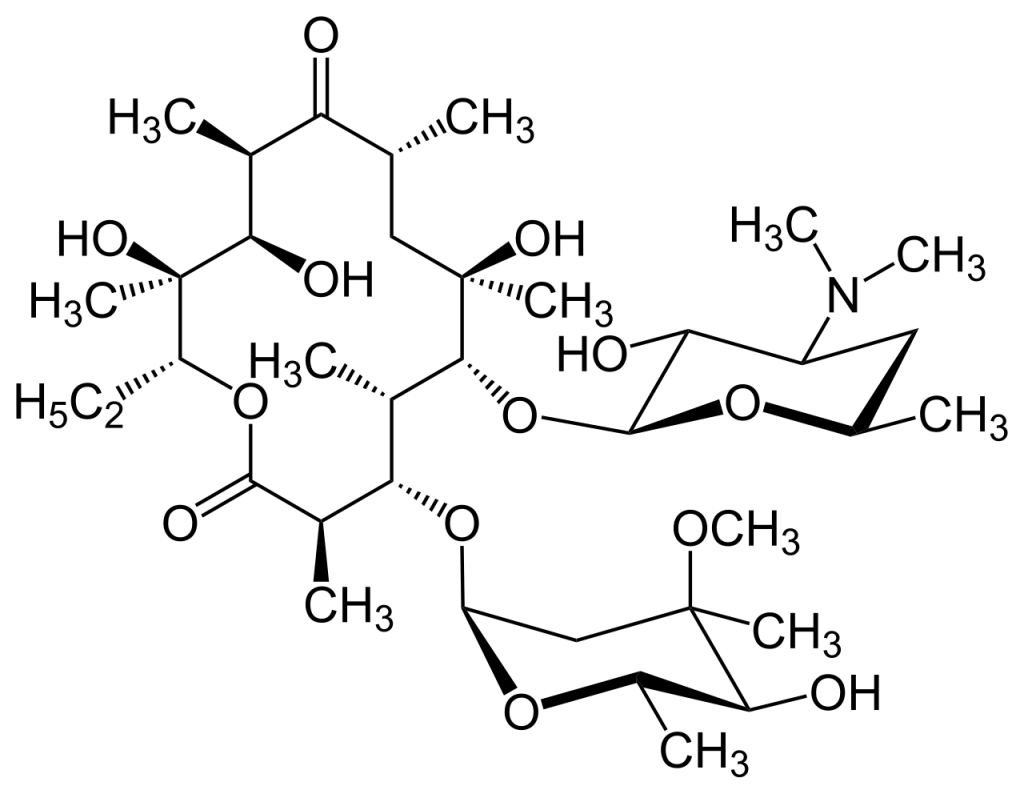
a) Amikacin
b) Warfarin
c) Fluticasone
d) Erythromycin
e) Penicillin
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 29: An aliphatic ring can be transformed into a cyclic structure with a lactone ring through which organic reaction?
a) Esterification
b) Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
c) Aldol condensation
d) Lactonization
e) Diels-Alder reaction
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
| Option | Description |
| A) Esterification | Formation of an ester bond between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid. |
| B) Friedel-Crafts Alkylation | Alkylation of aromatic rings using alkyl halides and a strong acid catalyst. |
| C) Aldol Condensation | Condensation of aldehydes and ketones to form a β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone. |
| D) Lactonization | Formation of a lactone ring by adding an oxygen across a carbon-carbon double bond in an aliphatic ring. |
| E) Diels-Alder Reaction | Cycloaddition reaction between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, forming a six-membered ring. |
Question 30: In a clinical trial of a drug to prevent migraines, 2 out of 100 people taking the drug experience a migraine (2%), compared with 4 out of 100 people taking a placebo (4%). Based on the given information, answer the following questions.
Question 30.1: What is the Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) in this clinical trial?
A) 0.5%
B) 1%
C) 2%
D) 3%
E) 4%
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
The Absolute Risk Reduction (ARR) is the difference in risk between the control group and the treatment group.
- ARR = 4% (placebo group) – 2% (treatment group) = 2%
Question 30.2: What is the Relative Risk Reduction (RRR) in this clinical trial?
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%
E) 125%
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
The Relative Risk Reduction (RRR) is the ARR divided by the risk in the control group.
- RRR = ARR / Risk in control group = 2% / 4% = 50%
Question 30.3: What is the Number Needed to Treat (NNT) in this clinical trial?
A) 25
B) 50
C) 75
D) 100
E) 200
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
The Number Needed to Treat (NNT) is the inverse of the ARR.
- NNT = 1 / ARR = 1 / 0.02 = 50
This article or question set is one of the many published for the preparation of PEBC EE Exam. Explore them all to get some practice before the exam. Also join our study group.

