Master the PEBC Evaluating Exam with Solved-Style Questions! Feeling stuck on PEBC practice tests? Don’t worry! This guide tackles a variety of realistic PEBC-style questions (like multiple choice) with in-depth explanations.
Feel free to ask any questions or doubts in the comment section below. All the best.
Table of Contents
Questions 1-10
Question 1: Where is the scaphoid bone located?
A. Wrist
B. Shoulder
C. Knee
D. Spine
E. Hips
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 2: Which headbone contains the nasal sinus?
A. Parietal
B. Frontal
C. Occipital
D. Temporal
E. Ethmoid
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Question 3: Common Drug Review (CDR) is under which organization?
A. NAPRA
B. Health Canada
C. CADTH
D. Federal Govenment
E. Provincial Government
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
CADTH is now ‘Canada Drug Agency’.
Attention to all the readers – I have published 15 question sets. I will add more questions to these 15 question sets. Please keep checking them.
Question 4: Protease is classified under which enzyme class?
A. Lyase
B. Hydrolase
C. Esterase
D. Isomerase
E. Ligase
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Question 5: Which cranial nerve is responsible for emesis?
A. Vagus nerve
B. Glossopharyngeal nerve
C. Olfactory nerve
D. Abducent nerve
E. Accessory nerve
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 6: Why is albumin added to insulin?
A. Buffer
B. Preservative
C. Solvent
D. Nutrient
E. Antiadsorbant
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Question 7: A lady who wants to quit smoking, smokes less than 5 cigarettes a day, and has oral ulcers as well as a history of schizophrenia. Which smoking cessation aid would be most appropriate for her considering her medical history?
A. Bupropion
B. Nicotine patch
C. varenicline
D. Nicotine gum
E. Behavioral therapy
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Bupropion is contraindicated in patients with seizures and schizophrenia. Varenicline should be used with caution as it has neuropsychiatric side effects like suicidal thoughts.
Question 8: What is the interaction between Codeine and Paroxetine?
A. Serotonin syndrome
B. Nothing will happen
C. Paroxetine will not work
D. Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
E. Codeine will not work
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Codeine is a prodrug which is metabolized by CYP2D6 and Paroxetine inhibits CYP2D6.
Question 9: A researcher is conducting a study. They want the mother of a 2-year-old child to remember what happened in her pregnancy. Which type of bias is this?
A. Recall bias
B. Selection bias
C. Publication bias
D. Lead time bias
E. Sampling bias
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
| Type of Bias | Description |
| Selection Bias | Sample or data isn’t representative of the population. |
| Confirmation Bias | Preferring information that confirms existing beliefs, ignoring contradictory evidence. |
| Sampling Bias | Sample isn’t randomly selected or doesn’t represent the population of interest adequately. |
| Observer Bias | Researcher’s expectations or beliefs influence interpretation or behavior of study subjects. |
| Reporting Bias | Selectively reporting positive results, omitting negative or inconclusive findings. |
| Measurement Bias | Inaccuracies or inconsistencies in measurement process, leading to systematic errors. |
| Publication Bias | Journals or researchers favor the publication of positive results, neglecting negative ones. |
| Recall Bias | Participants inaccurately remembering past events, affecting study outcomes. |
Question 10: A patient came with a prescription with his name but upon checking the pharmacist discovered these medicines didn’t belong to this patient. He asked the patient and found that the medicines are for his brother who doesn’t have insurance. If you accept this prescription you violate?
A. Veracity
B. Autonomy
C. Professional competency
D. Incapacity
E. Incompetence
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Please share this article ‘PEBC Pharmacist Evaluating Exam #13’ with your friends and in your study group. It will help me a lot. Thanks.
Questions 11-20
Question 11: Which one is the most complicated factor in assessing the UTI in women with CVD?
A. Sex
B. Pregnancy
C. Diabetes
D. Dash diet
E. Smoking
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
High sugar decreases immunity. Hence, this is a risk factor.
Question 12: Which vaccine is typically given to children at 1 year old with a booster dose at 4 to 6 years old?
A. MMR
B. Sabine Polio
C. DTaP
D. Influenza
E. Hepatitis B
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
MMR and Varicella are given at 12 – 18 months and 4 – 6 years.
Question 13: JT is a 29 year old male patient who takes Phenytoin 200 mg po tid. Because of swallowing difficulties his prescriber wants to change to Phenytoin liquid formulation. Phenytoin suspension is available in the strength of 125 mg/5ml. What will be the daily dose of Phenytoin suspension if the bioavailability of Phenytoin tablets is 92% and suspension is 100%?
A. 22 ml
B. 20 ml
C. 15 ml
D. 24 ml
E. 21.6 ml
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
The tablet contains 92% of Phenytoin and suspension contains 100%. So, 200 x 3 x 92% = 52mg of tablets.
125 mg —– 5ml
552 mg —– x
X = 21.6 ml = 7.2ml for every dose
Question 14: Which of the following is an advantage of using Taq polymerase in PCR?
A. Higher error rate
B. Less effective DNA denaturation
C. Lower accuracy
D. Thermostability
E. Slower process
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
Taq polymerase is used in polymerase chain reaction to make copies of DNA segment.
Question 15: A patient comes to the pharmacy to pick a prescription of Cefalexin suspension. Which of the following is not a counseling for this prescription?
A. Shake well
B. Refrigerate
C. Take on an empty stomach
D. Do not Refridgerate
E. Expect mild diarrhea
Click here to see the answer
Answer: D
Cephalexin, Amoxicillin, Amoxicillin/clav, Metronidazole, Erythromycin – All these in refrigerator at 2 – 8 oC.
Question 16: For which of the following symptoms would you refer a patient to doctor immediately?
A. Inflammation of the eye with purulent discharge for more than 2 days
B. Foot tinea fungal infection
C. Pain in the ear with drain for less than 24 hrs
D. Child 9-month-old with fever for less than 2 days
E. Coughing, and sneezing for less than 24 hours
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Children < 6 months of age with a fever should be assessed by healthcare Practitioners.
Children < 2 years – Refer if fever is for more than 72 hours.
Question 17: Which of the following is insured by Non Insured Health Benefits?
A. Prison
B. Inmate
C. Police
D. Refugee
E. Natives
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Natives and veterans are insured by NIHB.
Question 18: Which of the following is the first choice for thrombosis in cancer patients?
A. Chewable Aspirin
B. Heparin
C. Low dose ASA
D. Warfarin
E. Fondaparinux
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Fondaparinux and other Low molecular-weight heparins are preferred. Warfarin cannot be used as cancer patients are susceptible to wife fluctuations in INR. Oral anticoagulants like Apixaban are not preferred due to a high risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Question 19: Which of the following is the most lipophilic narcotic making it drug of choice for spinal anlagesia?
A. Meperidine
B. Sufentanil
C. Hydromorphone
D. Oxycodone
E. Morphine
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Fentanyl and Sufentanil are the most lipophilic opioids most widely used intrathecally.
Question 20: Which of the following is an example of a nosocomial infection?
A. Common cold
B. Chickenpox
C. Ventilator-acquired pneumonia
D. Seasonal influenza
E. Lyme disease
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Hospital-acquired pneumonia, Ventilator-associated pneumonia, Urinary tract infection, Gastroenteritis, Puerperal fever, and Central line-associated bloodstream infection are some examples of nosocomial infections.
Please share this article ‘PEBC Pharmacist Evaluating Exam #13’ with your friends and in your study group. It will help me a lot. Thanks.
Questions 21-30
Question 21: What is the mechanism of action of Gemcitabine?
A. Antimetabolite
B. Alkylating agent
C. Microtubule inhibitor
D. Monoclonal antibody
E. Aminoglycoside
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Other examples of cytidine analogues – Azacytidine, Cytarabine.
Question 22: which is a suitable method for measuring temperature in 2 years old child?
A. Oral
B. Rectal
C. Axilary
D. Ear
E. Tympanic
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
In children ≤ 5 years of age, rectal thermometry is the gold standard in Canada for definitive measurement of temperature.
Question 23: JtT is a 28 year old mother of a 9 months old child. She comes to the pharmacy asking for fever medicines for her child. Upon enquiring, she told that the child’s temperature is 38 °C and that she is concerned that her child might get febrile convulsion. Answer the following questions based on the given information.
Question 23.1: Which of the following medicines can be used to manage fever?
A. Acetaminophen
B. Ibuprofen
C. Frequent Cold Bathe
D. Wait and see if no improvement, refer
E. Refer to physician now
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 23.2: What to tell the mother about the seizure?
A. 20 % of children get febrile seizures on age 3 to 5 years
B. only children with neurological problems get febrile seizures
C. wait and see
D. Give Acetaminophen every 6 hours
E. Give Ibuprofen every 8 hours
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
A febrile seizure is a seizure associated with a high fever. They most commonly occur in children between the ages of 6 months and 5 years. If the seizure lasts longer than 5 minutes, call an ambulance. The child should be taken immediately to the nearest medical facility for diagnosis and treatment.
Question 24: From the given options, where is cholesterol found?
A. Plasma membrane
B. Cytoplasm
C. Nucleus
D. Mitochondria
E. Vacuoles
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Plasma membrane is made up of phospholipids and cholesterol.
Question 25: Which of the following is the most common gram-positive organism in bacterial meningitis?
A. Streptococcus Pneumonia
B. N. meningitidis
C. E. coli
D. Influenzae type b
E. Treponema palladium
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Question 26: You are a manager in a community pharmacy and you decided to give service at a price which only covers your cost and expenses. You decide to make this service with 10 cases per month, therefore you will have:
A. Increase in net profit
B. Increase in the revenue
C. Increase in the inventory
D. Decease in net profit
E. Increase in market share
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
You are making more revenue because you sold more items. However, you sold these items at their cost price so you did not make more net profit.
Question 27: How to overcome the issue of confounding factor in statistics?
A. Confounding factors hould be ignored
B. Subjects with confounding factors hould be ignored
C. Randomisation in the group to ensure confounding factor is evenly distributed
D. By using a complex statistical tool
E. Increase the sample size to minimize the impact fo compounding factor
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Strategies to reduce confounding are:
Randomization, Restriction, Matching, Stratification, Adjustment, Multivariate analysis.
Question 28: What happens when high uric acid is left untreated for a long time?
A. Osteoporosis
B. Osteoarthritis
C. Tophi
D. Migrane
E. Hypertension
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Question 29: The doctor is suspecting that his patient is suffering of hyperthyroidism, which assay
can be used to confirm his diagnostic?
A. Serum TSH
B. T4 in urine
C. Sensitive TSH
D. TSH in urine
E. T3 counts
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Sensitive TSH is more accurate than Serum TSH.
Question 30: Which of the following is the correct option for seborrheic dermatitis?
A. Triclosan
B. Sulphur
C. Ketoconazole
D. Tezarotene
E. Isotretenoin
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Please share this article ‘PEBC Pharmacist Evaluating Exam #13’ with your friends and in your study group. It will help me a lot. Thanks.
Questions 31-35
Question 31: Which of the following ions is involved in the pathophysiology of cystic fibrosis?
A. Chloride
B. Calcium
C. Sodium
D. Bicarbonate
E. Potassium
Click here to see the answer
Answer: A
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive type of genetic disorder of chromosome 7 in which there is an accumulation of mucus in the lungs. The defect in the CFTR gene, which encodes for a protein that functions as a chloride channel, & also regulates the flow of other ions across the apical surface of epithelial cells.
Question 32: Identiçfy the structure of the following drug
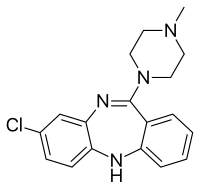
A. Azithromycin
B. Warfarin
C. Penicillin
D. Vitamin K
E. Clozapine
Click here to see the answer
Answer: E
Question 33: JT is a 54 year old male who comes to the pharmacy with a prescription of anticoagulant. He has CrCl < 15 ml/min. Which of the following drug is prescribed for JT?
A. Heparin
B. Warfarin
C. Enoxaparin
D. Dabigatran
E. Apixaban
Click here to see the answer
Answer: B
Warfarin has 100% hepatic metabolism and elimination. Hence, it is preferred in patients with impaired renal function or CrCl < 15 ml/min.
Question 34: What is the mechanism of action of Apixaban?
A. Vitamin K antagonist
B. Factor IIa inhibitor
C. Factor Xa inhibitor
D. TxA2 inhibitor
E. Irreversible platelet inhibitor
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Mnemonic – Apixaban has ‘Xa’ common in name as well as in mechanism of action, which is direct inhibition of factor Xa. Rivaroxaban is another example.
Question 35: Vitamin K is secreted from which of the following organs?
A. Lung
B. Kidney
C. Colon
D. Spleen
E. Liver
Click here to see the answer
Answer: C
Nailed these PEBC practice questions! This guide is your launchpad, but keep exploring resources & formats. Mock exams hone your timing. Study groups & textbooks? Yes, please! Conquer the PEBC & launch your Canadian pharmacy dream! ???????? #pharmacyexam

hello
can you please provide me with the study materials ?
i am willing to enter the exam on march